TELMDCARE
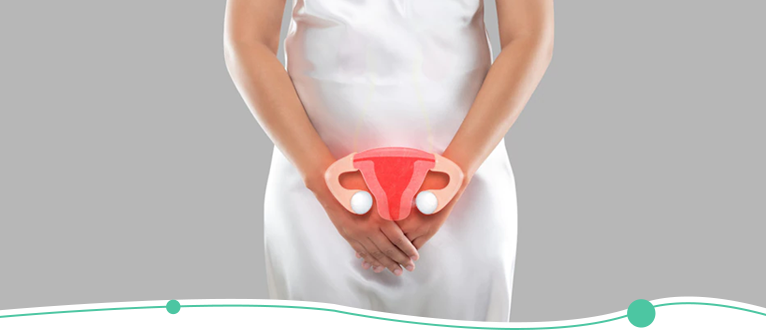
What is Bacterial
Vaginosis?
Bacterial Vaginosis is a fairly common and treatable condition afflicting women between the ages of 14 and 49. It is caused by an overgrowth of harmful bacteria, and it is generally treated with antibiotics. The infection may be present for several weeks after having sex or other activity that could have exposed you to these bacteria (such as douching or oral sex).
Seeking virtual doctor consultation for bacterial vaginosis treatment online is important as not doing so could have serious repercussions.
TELMDCARE
Is covered by many popular
insurance plans

TELMDCARE
Common Signs and Symptoms
- Irritation in the genital region
- Vaginal white, cloudy, or foamy discharge
- Inflamed, red, or swollen labia majora and minora
- A near-constant urge to urinate
- Pain during urination
- Pain during sexual intercourse
- Foul smells emanating from the vaginal region
How Online Doctor Appointments Help Treat Acute Vaginitis
Treatment for acute vaginitis largely depends on the cause behind it. If it’s bacterial vaginosis, the primary doctor will prescribe antibiotics or antibacterial creams. However, if it’s because of a yeast infection, then they might prescribe anti-fungal creams or medication like butoconazole and clotrimazole. Your online doctor consultation & prescription might be completely different from someone with the same condition because it will be specified to you. For instance, your virtual doctor is unlikely to prescribe you textbook medication if you are pregnant or allergic to certain ingredients.
What Happens If You Don’t
See A Primary Care Doctor?
Despite the harmless nature of this bacterial and fungal infection, it can have long-lasting effects, including:
Does Prevention Help?
Bacterial vaginosis is so common that you may get it at some point in your life. However, care could help you stay out of urgent care.
Help Treat Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial Vaginosis is a common infection of the vagina. It can be caused by bacteria that is found in the vagina and cervix, and it’s very common insexually active women. It’s important to remember that bacterial vaginosis is not a sexually transmitted disease however, having multiple sex partners or new partners may increases the chances of bacterial vaginosis.
It’s often treated with antibiotics, but some women find that they’re still experiencing symptoms after taking them for a long time. In these cases, it may be worth considering an appointment with an online doctor to get a prescription for an alternative treatment option.
Remember that the treatment for bacterial vaginosis largely depends on the cause behind it. Also our online doctor consultation & prescription might be completely different from someone with the same condition because it will be specified to you. For instance, your virtual doctor is unlikely to prescribe you textbook medication if you are pregnant or allergic to certain ingredients.
TELMDCARE
As Seen On


TELMEDCARE
What we treat
We treat a variety of acute and chronic conditions and provide expert medical advice and guidance for our patients.
Risk Factors Associated
With Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is an infection of the vagina that’s caused by the overgrowth of bacteria. You may not have BV if you’re otherwise healthy. You can get it from having sex with someone who has it or from douching too often.
There are a few risk factors for developing BV, including:
- Having a new sexual partner or having had sex within the last month with a new partner who doesn't use condoms
- Having sex with multiple partners in a short period or multiple partners in one day
- Using products (such as soap or wipes) that don't protect against STDs and pregnancy
If you’re at risk for developing BV, you should talk to our online doctor about safe and effective treatment for bacterial vaginosis immediately.
Complications Of The Condition
You’re probably wondering: what are the complications of bacterial vaginosis?
There are many, but some of the most common include:
- Bacterial vaginosis is thrice as common in infertile women as compared to fertile women indicating it might lead to infertility
- Bacterial vaginosis can increase your risk of HIV infection.
- It can also lead to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
- It can change your body's pH balance, which may lead to yeast infections and other conditions.

Medication services available 24/7 for adults and kids (3+)

Top quality, board-certified doctors

No insurance needed

Same-day prescriptions available*
TELMDCARE
Benefits Of Seeing A Virtual Doctor
For Bacterial Vaginosis
Online doctor appointments have several benefits over traditional medical appointments:
- You can schedule your appointment at any time of day or night. No waiting rooms or crowded exam rooms are waiting on you—you’re done in less than an hour while maintaining privacy.
- You don’t need a doctor’s referral to get in to see an online doctor; all you need is access to some basic information about your symptoms and medical history, and the doctor will get back to you as soon as possible.
- You’ll never have to worry about finding parking or dealing with long waits again!


TELMDCARE
How To Treat Bacterial
Vaginosis
Bacterial Vaginosis is a common vaginal infection caused by the bacteria Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis, and Ureaplasma urealyticum. This infection can cause itchiness, discharge, and odor. It’s also known as BV. When you have bacterial vaginosis, the acid in your vagina isn’t strong enough to kill off all the bad bacteria. That means those bacteria can multiply quickly and result in an unpleasant odor and discharge.If you’re experiencing any of the previously mentioned symptoms, your online doctor for bacterial vaginosis may recommend antibiotics. Antibiotics are effective in treating most cases of bacterial vaginosis. They can be used alone or as part of a treatment regimen that may include other medications and behavioral techniques. Antibiotics are usually prescribed for a short time, usually about 10 days, to kill bacteria and prevent reinfection. The most common antibiotics used to treat BV are metronidazole (flagyl) and clindamycin (cleocin). These drugs kill both types of bacteria that cause BV. However, some research suggests that the antibiotic rifampin (RIF) may be more effective than metronidazole or clindamycin in people with mild or moderate symptoms of BV. Similarly, ointments are also one of the most common treatments for bacterial vaginosis. These medications are applied to the vagina several times a day.
When Should I Call My Doctor?
If you have vaginal pain or a burning sensation in addition to these symptoms or have had unprotected sex recently, you should contact your doctor right away. If you have symptoms of BV that last for more than 10 days and/or return after treatment with antibiotics, see our online doctor again to discuss further treatment options.

Book Your Virtual Gynecology
Appointment
with TelMDCare
Get the best telemedicine doctor on call for bacterial vaginosis treatmentat TelMDCare, where you can avail the best online professional consultation at a discounted rate of $43, with a money-back guarantee, whether you are insured or not.
At our practice, you can make online doctor appointments for several conditions, and treat anything from ear infections to depression.
You can make online doctor appointments for several conditions at our practice and treat anything from ear infections to depression.
Not only are you entitled to a free follow-up, but our top doctors also work hand-in-hand with your local chemist to make sure you get your meds on time.
Sign up for an online medical consultation, or get in touch for enquiries.
TELMDCARE
Sign Up
Sign up and book an appointment with our specialists to get bacterial vaginosis treatment online today!
TELMDCARE
Common FAQs Related To Bacterial Vaginosis
How can I tell if I have bacterial vaginosis?
You will probably notice a white discharge from your vagina, which is usually accompanied by itching or irritation. You may also notice odorless, soapy-smelling vaginal secretions (mucus). Bacterial vaginosis can cause vulvovaginal symptoms such as redness, burning, and soreness. If you experience any of these symptoms, see our online doctorand get treatment for bacterial vaginosisright away!
What are some signs that I might have bacterial vaginosis?
The most common symptom of bacterial vaginosis is vaginal discharge characterized by a fishy odor, which can be watery or thick like yogurt. The discharge may be wet or sticky and can sometimes contain blood-tinged mucus. Other symptoms include increased vaginal discharge, burning during urination, and swelling in the labia minora.
What causes bacterial vaginosis?
Bacterial vaginosis is caused by an imbalance between good and bad bacteria in the vagina. The good bacteria help keep your vagina healthy by helping keep Candida albicans under control. The bad bacteria are usually present in small numbers but can multiply rapidly when they come in contact with other organisms or toxins—for example, from using scented feminine hygiene products or douches that contain perfumes or deodorants (which can irritate your vagina). These excess bad bacteria may also come from a partner who has had sex with someone who has bacterial vaginosis. The overgrowth of these bad germs can cause an unpleasant odor and thick yellowish discharge when you wipe after urinating or menstrual period, as well as itching around your vagina and soreness during intercourse.
Is bacterial vaginosis contagious?
No, bacterial vaginosis is not contagious. It is caused by a group of bacteria that live in the vagina and cause irritation and odor. These bacteria are not transmitted from person to person but can be spread through sexual contact or vaginal douching.



